Building alternative consensus trees and supertrees
Consensus tree and supertree inference methods synthesize collections of gene phylogenetic trees into comprehensive trees that preserve main topological features present in the input gene trees and include all taxa present in them.
Consensus tree and supertree inference methods synthesize collections of gene phylogenetic trees into comprehensive trees that preserve main topological features present in the input gene trees and include all taxa present in them. We introduced a new systematic method for inferring multiple alternative consensus trees and supertrees from a given set of phylogenetic trees, which can be defined either on the same set of taxa (case of multiple consensus trees) or on different sets of taxa with incomplete taxon overlap (case of multiple super-trees). The inferred alternative consensus trees and supertrees represent the most important evolutionary patterns characterizing a given set of gene phylogenies and are usually much better resolved than a single consensus tree or supertree inferred by traditional methods. Thus, a multiple consensus tree or supertree inference approach has the potential to build supertrees that retain much more plausible information from the input gene trees. A single consensus tree or supertree could be an appropriate representation of a given set of gene trees only if all of them, or a large majority of them, follow the same evolutionary patterns. The presented method allows one to identify ensembles of genes that underwent similar hor-izontal gene transfer, hybridization and intragenic/intergenic recombination events, or those that were affected by similar ancient duplication events during their evolution.
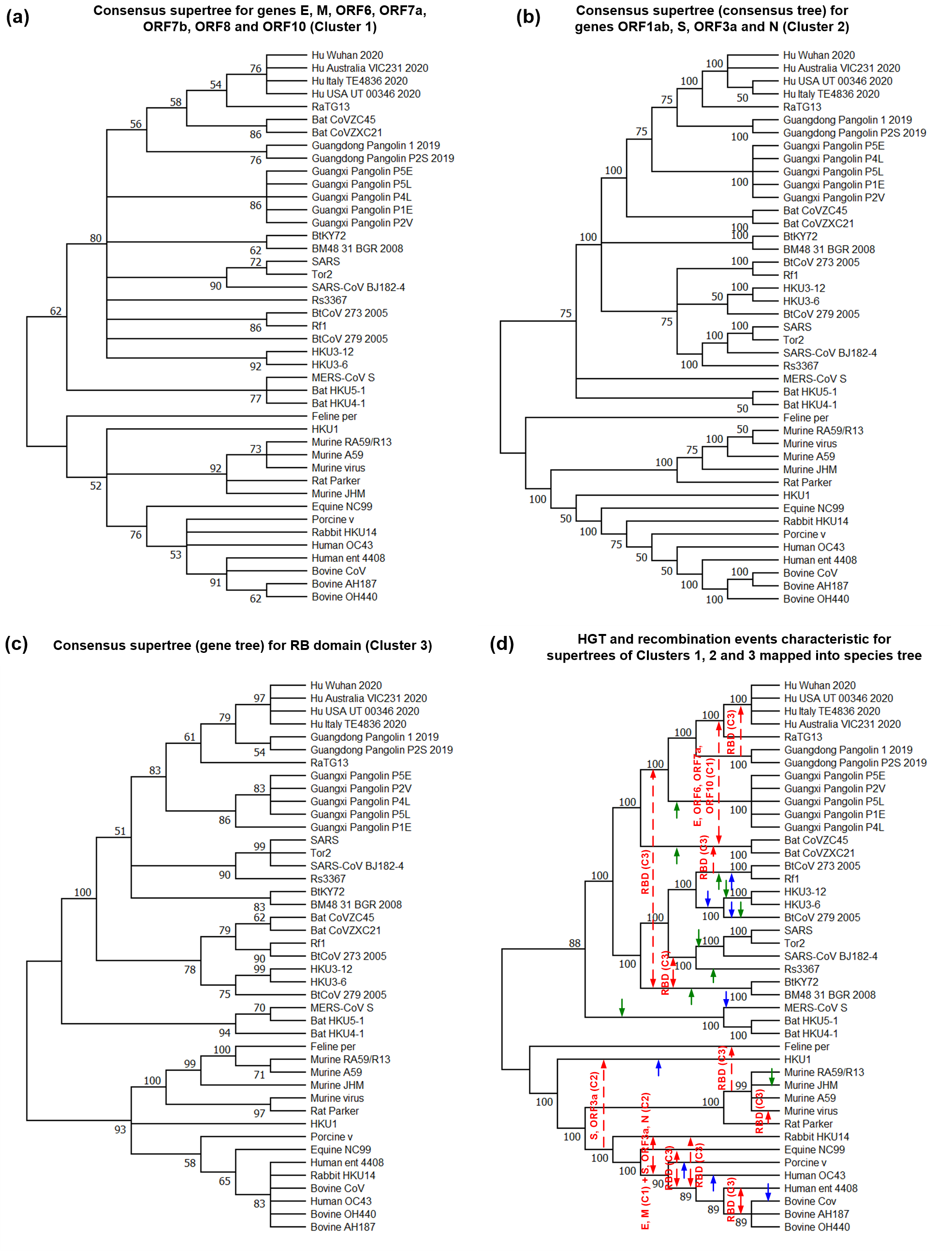
Source : Tahiri, Fichet, and Makarenkov (2022)
Related publications:
- Torquet, E., Jansson, J., & Tahiri, N. (2025). Graph-based method for constructing consensus trees. Proceedings in 15th International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics (ICBBB 2025), Bangkok, Thailand.
- Sifat, M. H. R., & Tahiri, N. (2024). A new algorithm for building comprehensive consensus tree. Proceedings in 4th workshop on Graphs and more Complex structures for Learning and Reasoning, Vancouver, Canada.
- Makarenkov, V., Barseghyan, G. S., & Tahiri, N. (2023). Inferring multiple consensus trees and supertrees using clustering: A review. Data Analysis and Optimization: In Honor of Boris Mirkin’s 80th Birthday, 191-213.
- Tahiri, N., & Koshkarov, A. (2022, July). New Metrics for Classifying Phylogenetic Trees Using K-means and the Symmetric Difference Metric. In Conference of the International Federation of Classification Societies (pp. 383-391). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Tahiri, N., Fichet, B., & Makarenkov, V. (2022). Building alternative consensus trees and supertrees using k-means and Robinson and Foulds distance. Bioinformatics, 38(13), 3367-3376.
- Tahiri, N; Willems, M; Makarenkov, V. (2018). A new fast method for inferring multiple consensus trees using k-medoids. BMC evolutionary biology. 18(48): 1-12.
FUNDING:
- Fonds de recherche du Québec - Nature et Technologie (FRQNT)